Posts tagged "design-patterns":
Differences of the builder pattern in Java and Python
In this post, we explore the differences in implementing the builder pattern in Java and Python.
1. Introduction
The builder design pattern 1, first introduced in the "Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software" (1994) 2, popularly known as Gang of Four (GoF), is classified as a creational design pattern. This post focuses on its application in Java and Python.
At my current job we are using different programming languages. We decided to use the buildern pattern for one of our python microservices. While writing the buildern pattern in python, the team brought their "java style" to the python code. However, there is a pythonic way to write it and save some lines of code. This is the story behind this post.
2. Language features in Java and Python
Let's first examine the features of each language that we will later use to implement the design patterns in Python and Java. Python supports function default arguments 3 and named parameters 4, while Java supports function overloading 5.
The following examples demonstrates default arguments:
# Function with default arguments def calculate_area(length, width=5): area = length * width print(f"Area: {area}") # Using the function with both parameters calculate_area(8, 4) # Using the function with the default value for 'width' calculate_area(10) # Width defaults to 5 # You can still explicitly provide a value for 'width' calculate_area(6, 3)
The following Python example demonstrates both default arguments and named parameters:
# Function with named parameters def print_user_info(name, age, city="Unknown", country="Unknown"): print(f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}, City: {city}, Country: {country}") # Using named parameters print_user_info(name="John", age=25, city="New York", country="USA") # Omitting some named parameters (using defaults) print_user_info(name="Alice", age=30) # Mixing ordered and named parameters print_user_info("Bob", 28, country="Canada")
The following Java example shows how function overloading works:
// Java program to demonstrate working of method overloading in Java public class Person { private String firstName; private String lastName; // Person constructor with two arguments, the first and last name. public Person(String firstName, String lastName) { this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; } // Another constructor, this time with a single argument, the first name. public Person(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Using constructor with two parameters Person person1 = new Person("John", "Doe"); // Using constructor with one parameter Person person2 = new Person("John"); } }
3. The builder pattern in Java 6
Factories and constructors share a limitation: they do not scale well to large numbers of optional parameters. Consider the case of a class representing the ingredients of a Pizza. Most ingredients have nonzero values for only a few of these optional fields.
What sort of constructors or static factories should you write for such a class? Traditionally, programmers have used the telescoping constructor pattern, in which you provide a constructor with only the required parameters, another with a single optional parameter, a third with two optional parameters, and so on, culminating in a constructor with all the optional parameters. Here’s how it looks in practice. For brevity’s sake, only three optional cheese fields are shown:
1: public class Pizza { 2: private final int dough; // 100g, 200g, 300g required 3: private final int mozarella; // 100g, 200g, 300g optional 4: private final int parmesan; // 50g, 100g, 150g optional 5: private final int gorgonzola; // 50g, 100g, 150g optional 6: 7: public Pizza(int dough) { 8: this(dough, 0, 0, 0); 9: } 10: 11: public Pizza(int dough, int mozarella) { 12: this(dough, mozarella, 0, 0); 13: } 14: 15: public Pizza(int dough, int mozarella, int parmesan) { 16: this(dough, mozarella, parmesan, 0); 17: } 18: 19: public Pizza(int dough, int mozarella, int parmesan, int gorgonzola) { 20: this.dough = dough; 21: this.mozarella = mozarella; 22: this.parmesan = parmesan; 23: this.gorgonzola = gorgonzola; 24: } 25: }
When you want to create an instance, you use the constructor with the shortest parameter list containing all the parameters you want to set:
Pizza margarita = new Pizza(200, 200);
In short, the telescoping constructor pattern works, but it is hard to write client code when there are many parameters, and harder still to read it.
Luckily, the builder pattern helps us with the readability and tediousness of the code. Instead of making the desired object directly, the client calls a constructor with all of the required parameters and gets a builder object. Then the client calls setter-like methods on the builder object to set each optional parameter of interest. Finally, the client calls a parameterless build method to generate the object, which is typically immutable. The builder is typically a static member class of the class it builds. Here’s how it looks in practice:
public class Pizza { private final int dough; // 100g, 200g, 300g required private final int mozarella; // 100g, 200g, 300g optional private final int parmesan; // 50g, 100g, 150g optional private final int gorgonzola; // 50g, 100g, 150g optional public static class Builder { // Required parameters private final int dough; // Optional parameters - initialized to default values private int mozarella = 0; private int parmesan = 0; private int gorgonzola = 0; public Builder(int dough) { this.dough = dough; } public Builder setMozarella(int val) { mozarella = val; return this; } public Pizza build() { return new Pizza(this); } } private Pizza(Builder builder) { dough = builder.dough; mozarella = builder.mozarella; parmesan = builder.parmesan; gorgonzola = builder.gorgonzola; } }
The Pizza class is immutable, and all parameter default values are in one place. The builder’s setter methods return the builder itself so that invocations can be chained. Here’s how the client code looks:
Pizza pizza = new Pizza.Builder(200).setMozarella(200).setGorgonzola(50).build();
The Builder pattern simulates default arguments and named parameters as found in Python and eludes the telescoping pattern avoiding function overloading.
4. The builder pattern in Python
In python, we just simply leverage the language support for named parameters and default values as explained in 2 to write pythonic code for the builder pattern.
class Pizza: """ Pizza class to represent a pizza with its ingredients. To set the ingredients the builder pattern is used. """ def __init__( self, dough: int, mozarella: int = 0, parmesan: int = 0, gorgonzola: int = 0, ) -> None: self.dough = dough self.mozarella = mozarella self.parmesan = parmesan self.gorgonzola = gorgonzola
This time we do not need to concatenate calls, nor call a build method to instantiate a pizza object.
pizza = Pizza(200, mozarella=200, gorgonzola=50)
5. Summary
Exploring the Builder Pattern in Java and Python, we uncovered language-specific nuances. While Java employs an inner builder class to simulate features like named parameters and default arguments found natively in Python, the latter provides a more concise and idiomatic approach. The post contrasts these implementations, offering insights into the divergent paths each language takes when applying the Builder Pattern.
Footnotes:
Based on the excellent book "Effective Java: Programming Language Guide" (Third edition 2017) from Joshua Bloch. Item 2: Consider a builder when faced with many constructor paramters.
Java singleton
Not long time ago, I discovered in Java it is possible to implement a Singleton with an Enum. And not only that, it is the recommended way to implement them!
In this post, we explore the best practices when implementing the singleton pattern in Java.
1. Introduction
The following text is extracted from the wikipedia 1:
In software engineering, the singleton pattern is a software design pattern that restricts the instantiation of a class to a singular instance. One of the well-known "Gang of Four" design patterns 2, which describes how to solve recurring problems in object-oriented software, the pattern is useful when exactly one object is needed to coordinate actions across a system.
More specifically, the singleton pattern allows objects to:
- Ensure they only have one instance
- Provide easy access to that instance
- Control their instantiation (for example, hiding the constructors of a class)
The term comes from the mathematical concept of a singleton 3.
In this post, we'll dive into the best practices for implementing the singleton pattern in Java, considering key features such as concurrency, reflection, and serialization.
2. Java features to consider when creating a singleton
2.1. Concurrency
When creating a singleton in Java we need to make sure it is thread safe4. That is, when two or more threads instantiate a singleton only a single instance is created.
For this purpose, we will leverage the static keywork. The keyword static means that the particular member belongs to a type itself, rather than to an instance of that type.
From the java docs5: "If a field is declared static, there exists exactly one incarnation of the field, no matter how many instances (possibly zero) of the class may eventually be created.
2.2. Reflection
In the later examples, we will make use of a private contructor to implement the Singleton. With the help of Reflection6, an attacker could modify the runtime behaviour of the application modifying the accessibility of the private constructor to public. In other words, with the help of Reflection it would be possible to create a second instance of the class.
2.3. Serialization
Serialization is the process of translating an object into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later. See figure 1.
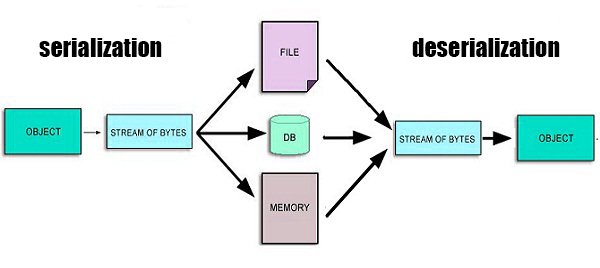
In Java, serializability of a class is enabled by the class implementing the java.io.Serializable interface.
Now, imagine your application serializes your singleton instance, so far so good, a stream of bytes has been created. However, when your application deserialize the same stream of bytes, it might end creating a new instance, leading, in the case of our example, to have two different instances!
Therefore we need to be carefull with Serialization when implementing our Singleton.
3. Singleton implementation
The two common ways of implementing singletons are based on keeping the constructor private and exporting a public static member to provide access to the instance.
In this first approach, the member INSTANCE is a final static field. The private constructor is called only once, to initialize the public static final field Spyderman.INSTANCE.
// Singleton with public final field public class Spyderman { public static final Spyderman INSTANCE = new Spyderman(); private Spyderman() { ... } public void withGreatPowerComesGreatResponsibility() { ... } }
Thanks to the static final INSTANCE, we make sure the singleton is thread safe 2.1. However, an attacker could change thanks to reflection 2.2 the accessibility to the constructor, making it public or private and invoking it twice or more. We can defend ourselves against this attack making the constructor to throw an exception if it is invoked to create a second instance.
In the second approach to implement sigletons, the public member is a static method:
// Singleton with static factory public class Spyderman { private static final Spyderman INSTANCE = new Spyderman(); private Spyderman() { ... } public static Spyderman getInstance() { return INSTANCE; } public void withGreatPowerComesGreatResponsibility() { ... } }
All calls to Spyderman.getInstance() return the same object reference. Same as the first example, it is thread safe thanks to the statics fields and it has the same caveat with reflection.
This second implementation is the prefered one, as it is more flexible, allowing the developer to remove the singleton property without changing the API as well as implement one singleton per thread or incorparating generics.
Now, if we need to make one of the above approaches Serializable adding implements Serializable, we need to modify our code to keep the singleton guarantee. Otherwise, each time a serialized instance is deserialized, as explained before 2.3, a new instance will be created. The solution would be to declare all instance fields transient and implement the readResolve method. We can find examples of this in the java.util.Collections7 file.
There is a third approach to the Singleton pattern, where we do not have to deal with thread safety, reflection nor serialization. It is the enum approach:
// Enum singleton - the preferred approach public enum Spyderman { INSTANCE; public void withGreatPowerComesGreatResponsibility() { ... } }
This approach look at first a bit inuntuituve. But lets check it properties. Every enum constant is always implicitly public static final which make it thread safe. There is no constructor that can be called by the developer so it makes it safe againts reflection attacks and as per documentation8 Enums are Serializable and special methods like readResolve are ignored.
The main disadvante is that Enums can not extend a superclass other than Enum, luckily, we can implement other interfaces.
4. Summary
We have seen why the Enum approach is often the best way to implement a singleton. The jvm provides the serialization and the protection against multiple instantiation and reflection attacks for free.
